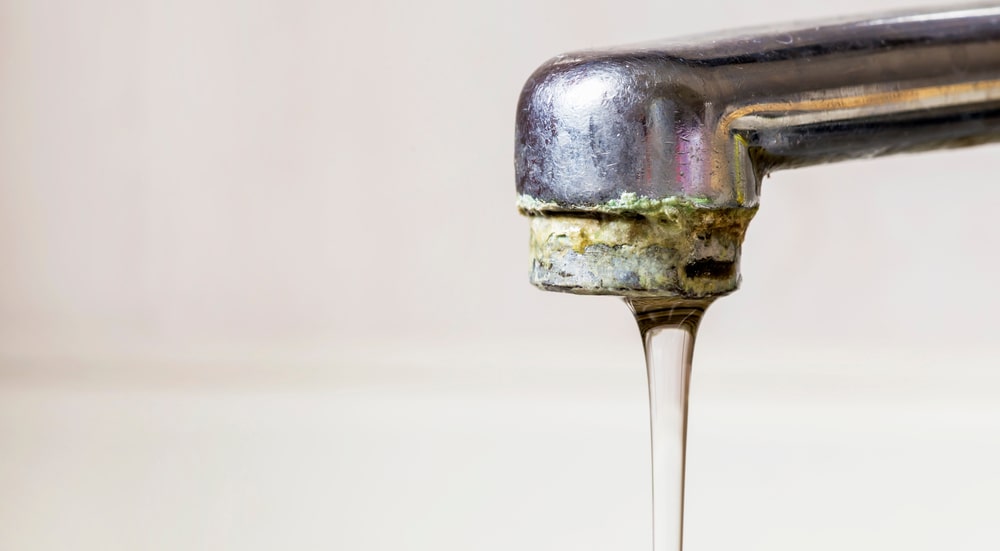
The water supply in this location naturally contains hard water. It is brought on by the presence of minerals (calcium and magnesium) that our source water picked up while travelling through the ground; in our region, it is primarily limestone rock.
In accordance with recommendations from the World Health Organization (WHO), water is deemed “hard” and will cause scale when the concentration of calcium carbonate is greater than 200 mg/l (mg/l or parts per million).

| Level of calcium carbonate (mg/l) | Classification |
|---|---|
| 0-50 | Soft |
| 51-100 | Moderately soft |
| 101-150 | Slightly hard |
| 151-200 | Moderately hard |
| 201-300 | Hard |
| Above 300 | Very hard |
Even though there may be seasonal variations, all of the water in the Excellent Water area is considered to be hard or extremely hard.
Although hard water can cause issues in the home, it is perfectly safe and doesn’t indicate that your water supply isn’t of high enough quality.
The “hardness” of your water is determined by naturally existing minerals like calcium and magnesium.
Since hard water does not present a health risk, there is no water quality standard in place to regulate it.
Some people find that it can dry out their skin, which can make pre-existing skin conditions worse.
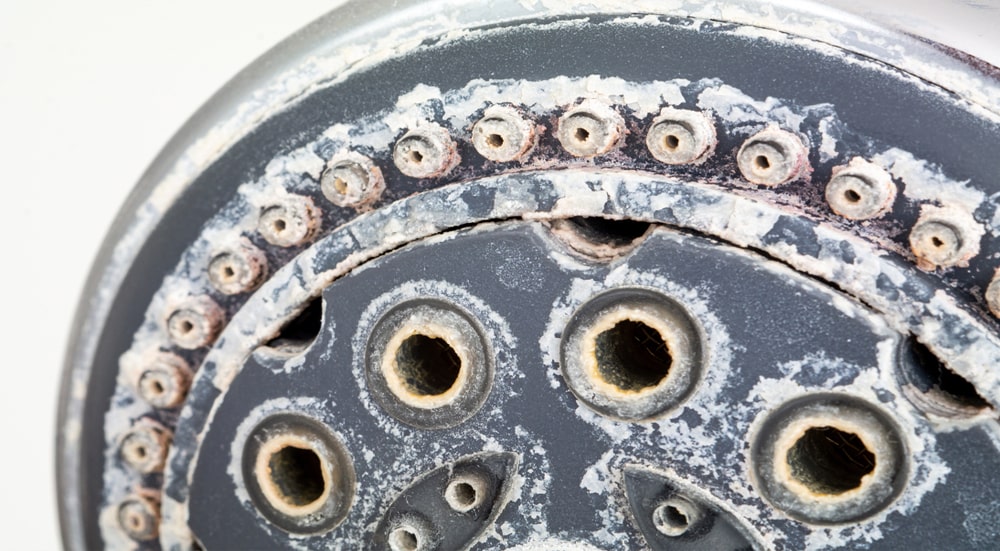

Physical water conditioners and inhibitors of scale :
The most common sorts area unit electrical water conditioners and magnetic water conditioners; each sorts operate in an exceedingly similar means. once H2O is heated limescale forms as small crystals. the form of those crystals promotes the build-up of limescale. In theory, physical water conditioners modification the form of the limescale crystals, that prevents them from protruding to surfaces effort them suspended within the water. This result is believed to be temporary, thus for best results, the device ought to be fitted as shut as doable to the unit heating the water. Physical water conditioners don’t take away the metal and metal minerals from the water. As they are doing not soften the water you’re unlikely to note any impact on quantity|the quantity|the number} of soap or detergent used or a discount within the amount of limescale forming in your kettle. However, as a result of they are doing not modification the chemistry of the water it remains safe to drink.
Phosphate is the chemical conditioner dose that is used the most frequently. The calcium and magnesium minerals mix with the polyphosphate, which prevents them from precipitating out of solution, and thus prevents the devices from working by adding a small amount to the water. To guarantee they do not impact the quality of your drinking water, these devices should always be installed by a certified individual.
By using water softeners to remove the calcium and magnesium minerals from the water, limescale is prevented from forming when the water is heated. The result is long-lasting, in contrast to physical water conditioners. You will also use less soap and detergent as a result. Ion-exchange salt softeners and reverse osmosis systems are the two most prevalent types of equipment installed in residential buildings.
Calcium and magnesium minerals are swapped out for sodium in ion exchange salt softeners. Resin beads inside the device allow the water to travel through them. In the water, the calcium and magnesium ions exchange places with the sodium ions on the resin. Eventually, not enough sodium ions are present, and regeneration of the resin is required. By flushing the resin with a salt solution that replaces the sodium ions, this is accomplished. This kind of softener is simple to instal and reasonably inexpensive to buy and operate. However, it is advised that unsoftened water be available from at least one tap in the building for drinking and cooking as they raise the sodium content of the water.
Other minerals and metals that can be present in the water are also removed by reverse osmosis systems, in addition to calcium and magnesium. Through the use of a semi-permeable membrane, they force water through. The membrane is filled with numerous small openings that can pass water molecules but not larger ones. When compared to ion-exchange softeners, this kind of technology is typically more expensive and uses more energy.
Both kinds of softeners should be fitted in compliance with the Water Supply (Water Fittings) Regulations of 1999 by a qualified individual. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations when using and maintaining home treatment equipment. Additionally, it is advised that a bypass be made to supply you with water in the event that the appliance breaks down or malfunctions.
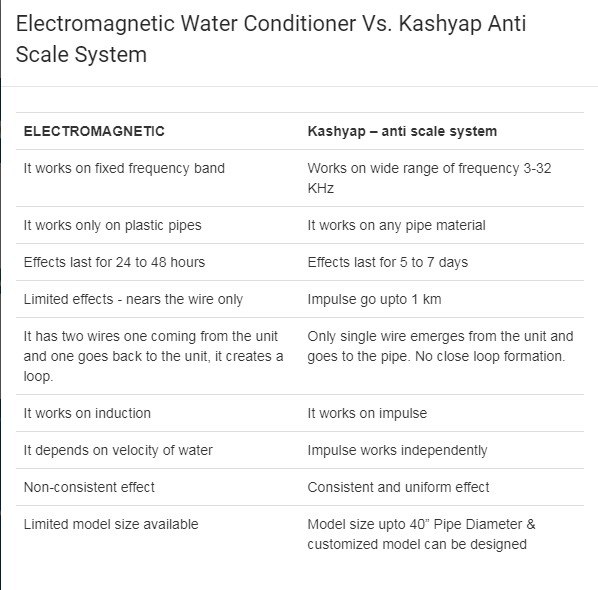
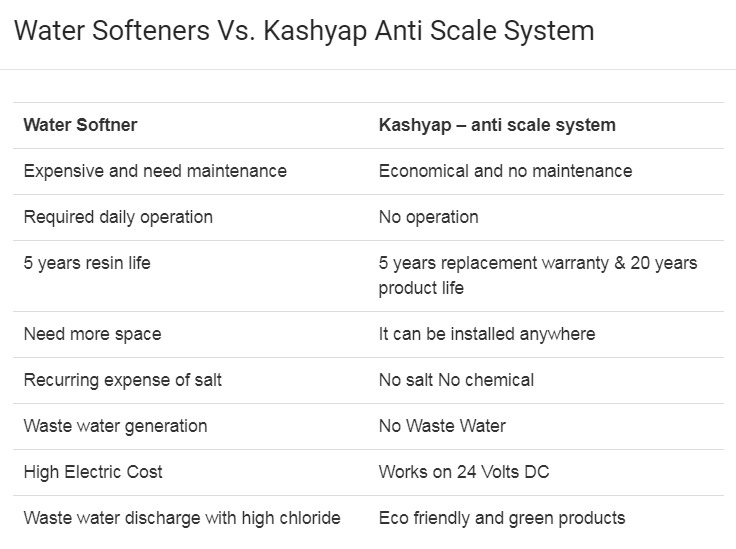
Kashyap Anti Scale Systems, offered by Excellent Water Technology, are part of our innovative solutions for hard water treatment. As a leading water solution company, we are dedicated to improving performance and product quality while delivering exceptional value to our customers.
Copyrighted © 2025 Excellent Water Technology. All Rights Reserved.